Created: 2023-01-12 19:59
Status: #concept
Subject: Programming
Tags: C Memory Memory Address C Data Type Pointer Arithmetic Dynamic Memory Allocation
Pointer
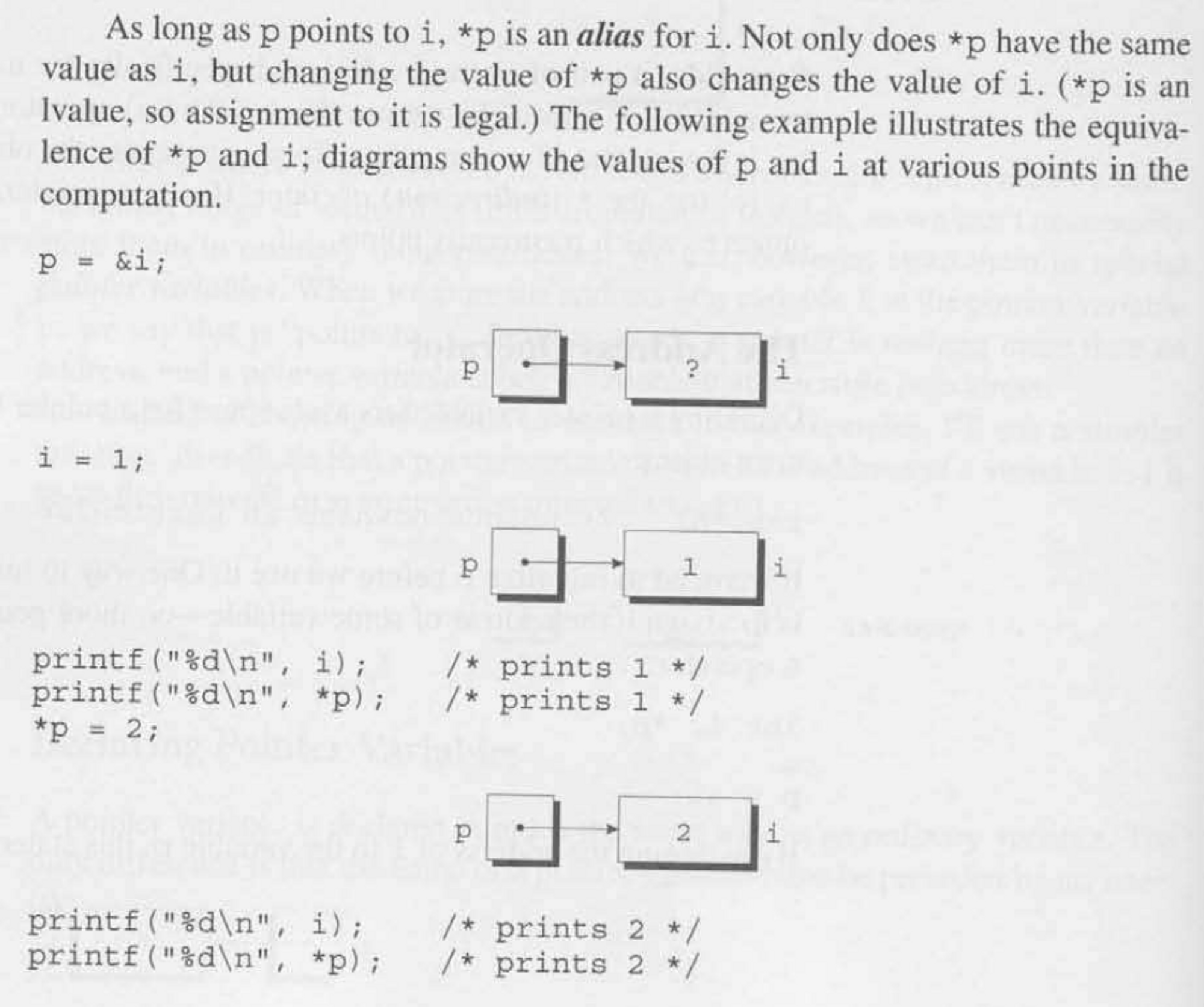
We call them aliases to the variables they point to because we can modify the pointer variable's value and it will affect the original variable.
- It may also refer to the Integer data type that represents a Memory Address.
- They are important in order to do Pass-by-Reference with Functions.
Declaration Syntax
int *p; // declares the Integer Pointer Variable named 'p'
p = &i; // assign the Memory Address of {i} into the Pointer Variable {p}
- The sizeof Operator on a pointer variable yields 8 Bytes in 64-bit computers.
- Pointer Variables can only point to compatible C Data Type, specified by their declaration.
- Pointer Variables may point to other Pointer Variables.
- They may also point to Functions.
float *f; // only points to float
double *d; // only points to double
char *r; // only points to characters
int **p;
// A Pointer Variable, named 'p', that points to an Integer Pointer Variable
Referencing
int num = 5; // assign 5 to the variable {num}
int *p = # // extract the address of {num} and assign it to pointer {p}
Deferencing
Likewise, we need to Dereference Pointer Variables in order to access the value of the Variable it is pointing to.
int num = 5, *p = # // let the pointer {p} point to the address of {num}
printf("%d", *p); // print the value pointed to by {p}
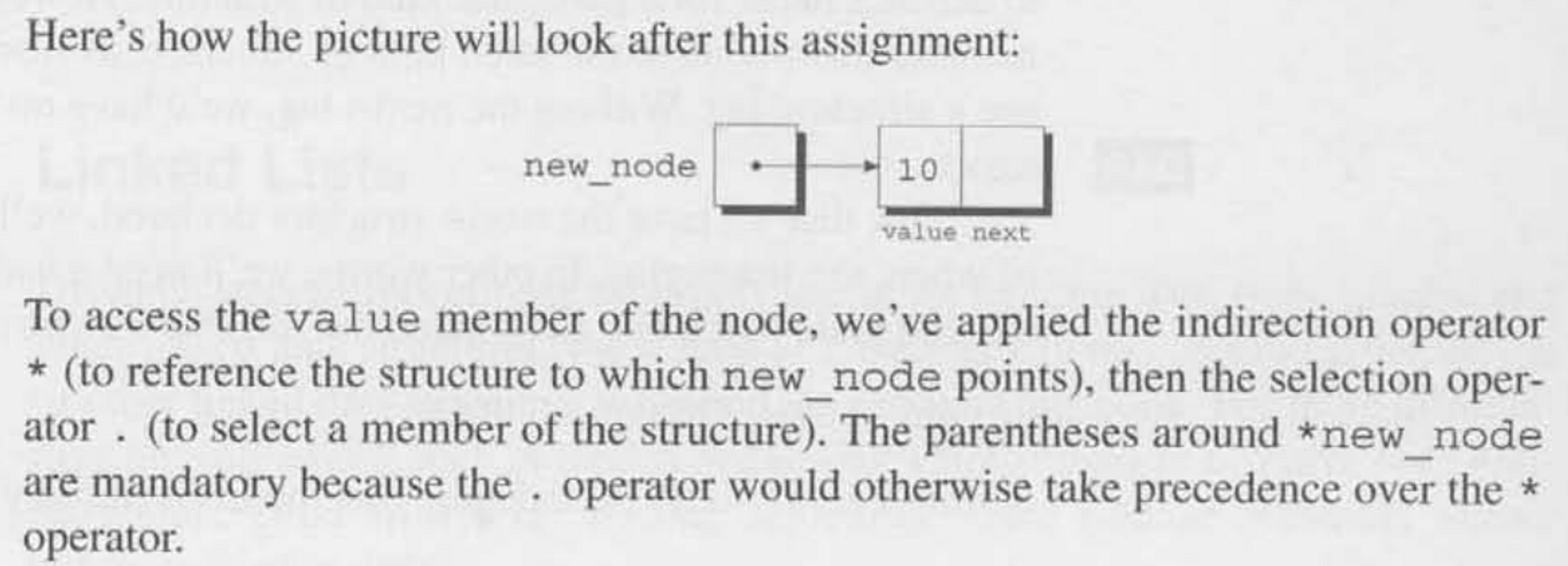
The Arrow Operator ->
(*new_node).value = 10; // dereference new_node struct & edit the 'value' member
new_node->value = 10; // is equivalent to above
/*** WRONG ***/
*new_node.value = 10; // ERROR: is equivalent to *(new_node.value)
new_node->next = first; // let's the new_node's 'next' member point to the old first
first = new_node; // we then keep track of the first node to be new_node
Assignment
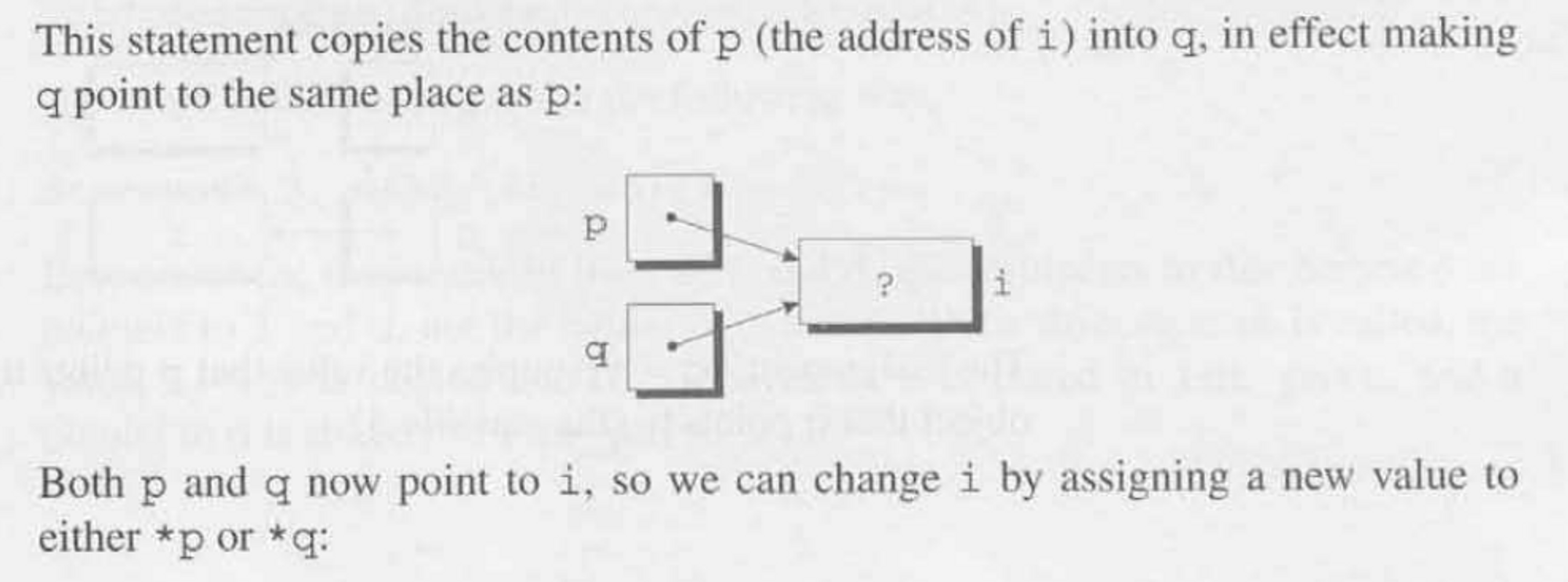
We may also use an existing pointer as a Memory Address for Pointer Assignment.
int i, j, *p, *q;
p = &i; // this is pointer assignment where the address of {i} is stored in {p}
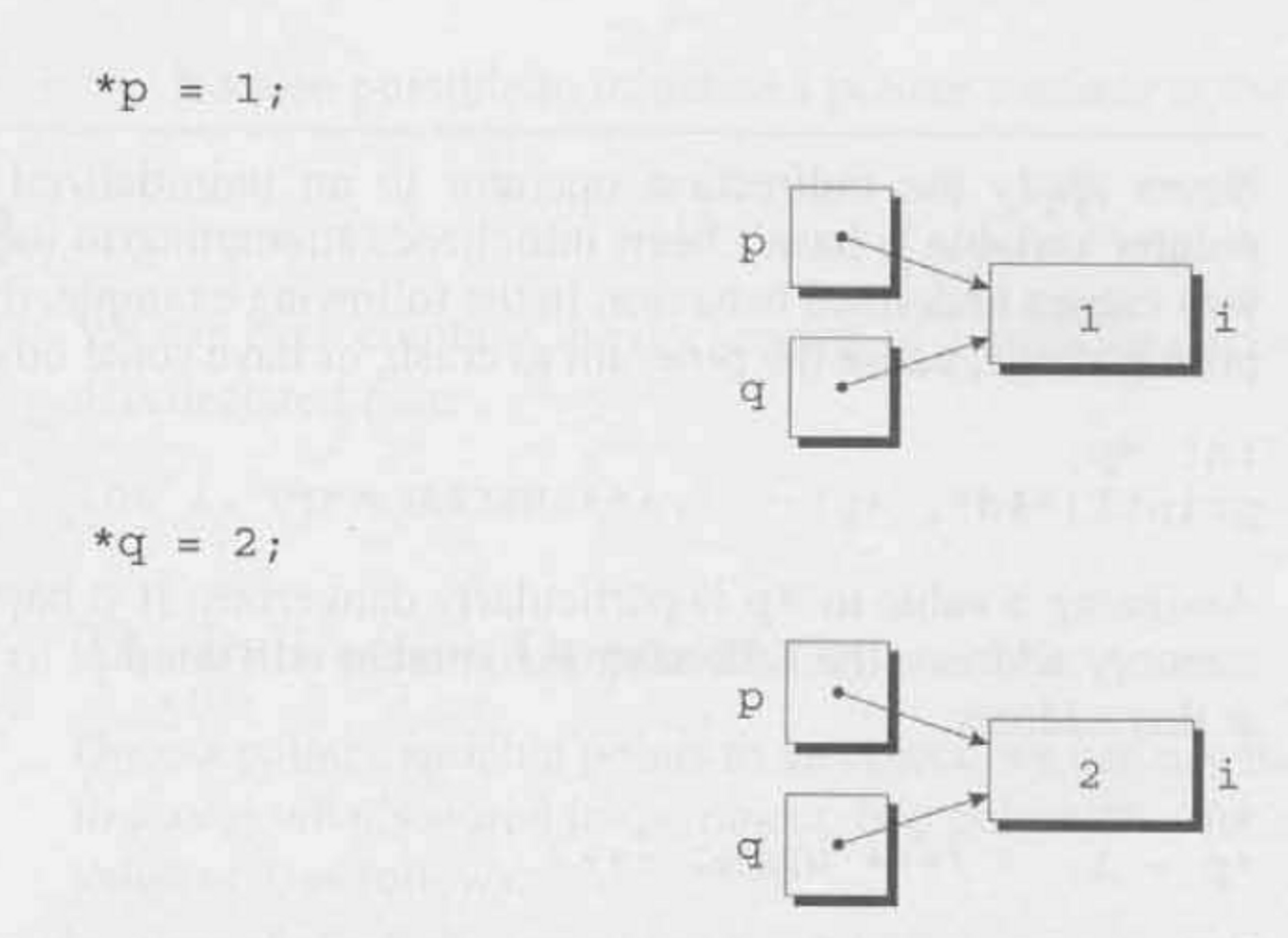
q = p; // this copies the contents of {p} (memory address pointer) into {q}
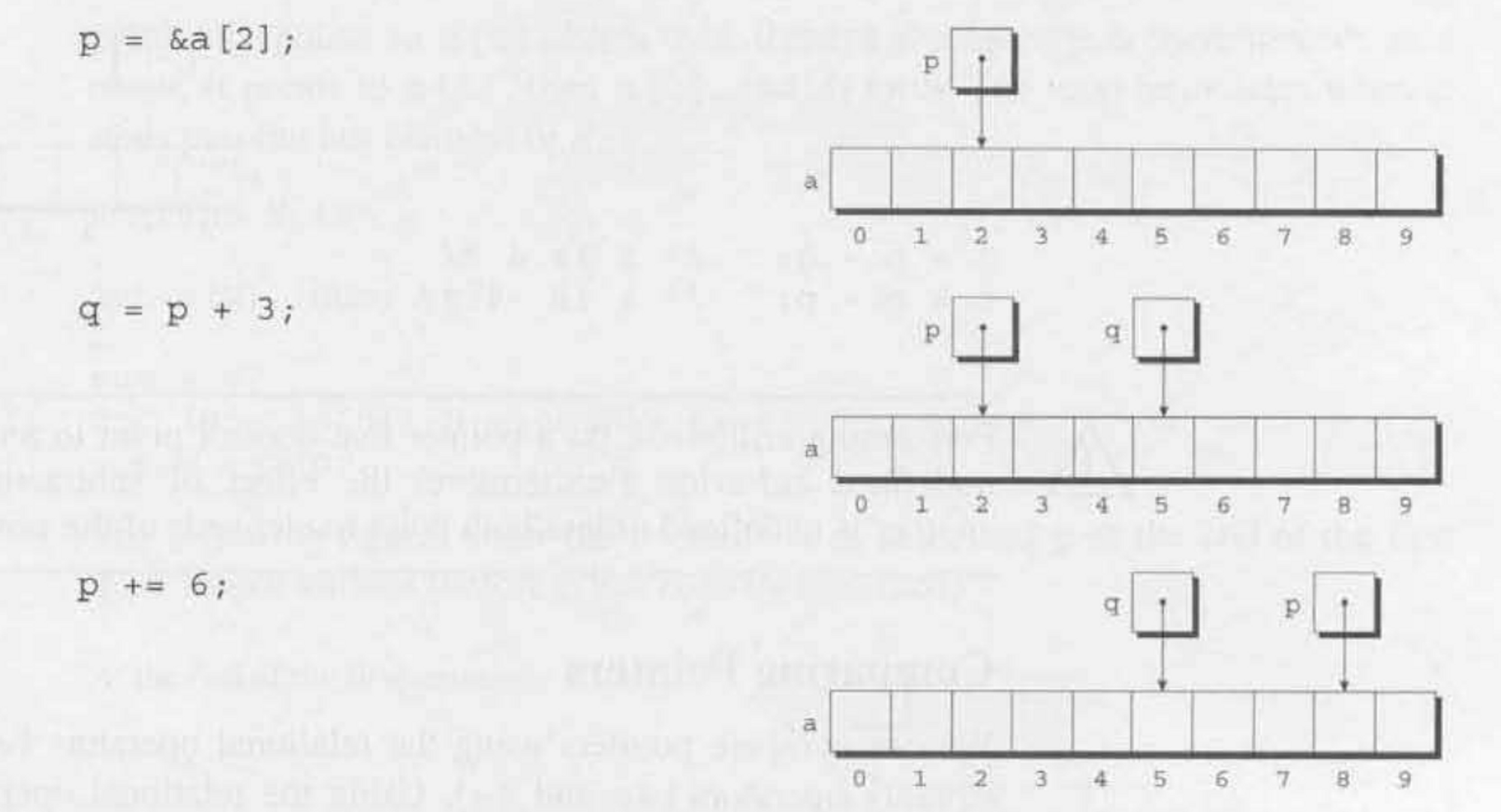
Addition or Subtraction
Using
+ and - on pointer variables performs pointer arithmetic.
- Adding or Subtracting an Integer
Nto a pointer shifts itN * sizeof(pointer's_object) - Subtracting a Pointer from another evaluates to the
Difference of addresses / sizeof(pointer's_object)
For more info, see Pointer Arithmetic.
Returning a Pointer from a Function
We have to prepend a
* before the Function Identifier in order to let a function return a Memory Address to the Function Call.
We need to return a pointer variable
p or a Memory Address &num in these functions because they return a memory address and not a value.
%20Function.png)
Pointers to Pointers (double pointers)
We have to set the function paramater to a Pointer to a Pointer Variable
**p.
- We have to pass in the address of the old pointer
&old_ptrvariable to the function call. - We have to dereference the
**Variable to access the Pointer*Variable using*old_pointer.
These are very useful when making Linked Lists.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void modifyPointer(int **old_array) // using Compound Literals
{
int *new_array = (int []){4,5,6};
*old_array = new_array;
}
void modifyPointer(int **old_array) // an alternative using malloc
{
int *new_array;
new_array = malloc(sizeof(int) * 3);
new_array[0] = 4, new_array[1] = 5, new_array[2] = 6;
*old_array = new_array;
}
int main(void)
{
int *old_array = (int []){1,2,3}; // it won't work if this was an array[]
printf("%d %d %d\n", old_array[0], old_array[1], old_array[2]);
modifyPointer(&old_array);
printf("%d %d %d\n", old_array[0], old_array[1], old_array[2]);
}
References
- C Programming, A Modern Approach, 2nd Edition, Chapter 11.1 - 11.3
- gcc Documentation & Options