Created: 2023-09-27 20:09
Status: #concept
Subject: Programming
Tags: Java Java Class Multithreading CPU Process Parallel Programming
Java Thread
It is a class that we can extend and
@Override the public void run() method in order to run the function body in a dedicated thread.
Each thread will occupy a CPU core until the run() stops or when we do Thread.sleep(ms) inside it.
- we use
ThreadInstance.start()to branch out the main execution thread into a new one. - any Java Exception thrown inside a thread is isolated while the other threads can still work.
Threads do not execute in order due to how a CPU does a round-robin for time-sharing, so there beware of Race Conditions.
public class Loop extends Thread {
public final String label;
public Loop(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; true; i++) {
System.out.println("Thread " + label + ": " + i);
}
}
}
We use it like so:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loop loop1 = new Loop("1");
Loop loop2 = new Loop("2");
Loop loop3 = new Loop("3");
loop1.start();
loop2.start();
loop3.start();
}
}
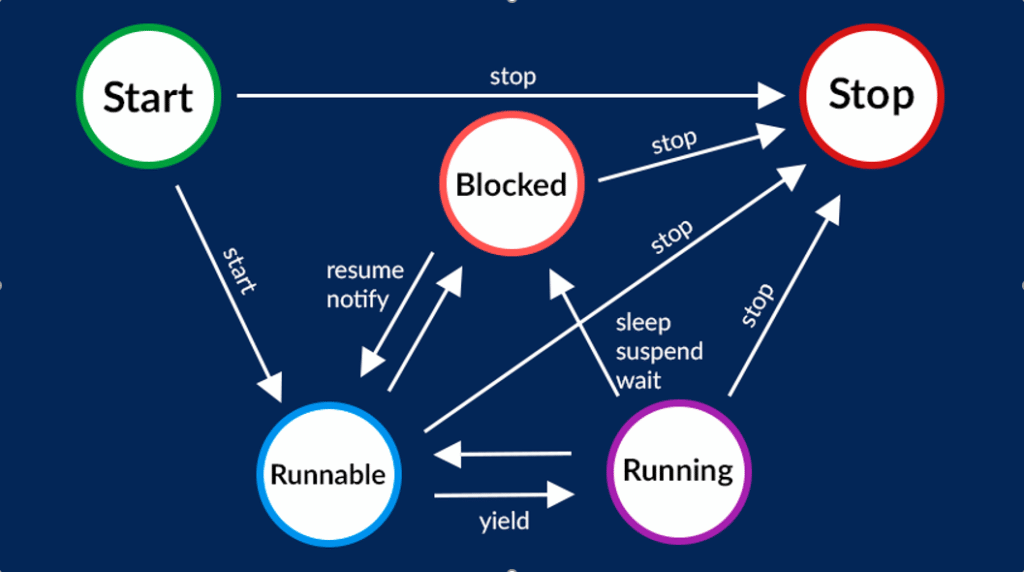
Instance Methods
.start()- executes the
public void runmethod of a passed-inRunnableor from extending & overridingThread.
- executes the
.yield()- acts like
setTimeout(Runnable, 0)and waits for other threads to run before running again.
- acts like
.join()- waits until the instance dies before continuing.
- we can call
t.isAlive()to check if the thread is still running. - acts like
await t.
- we can call
- waits until the instance dies before continuing.
Using Thread.sleep(ms)
When we want to unblock the thread, we can use
Thread.sleep(int ms) inside the public void run method.
- it will allow other code to run on the thread until the
msis elapsed based on the system clock: freeing up CPU utilization. - when we use it, we need to surround it within a
try-catchto handle theInterruptedExceptionJava Exception.
Handling InterruptedException
This exception is thrown when the thread stopped early or the instance method
ThreadInstance.interrupt() was called.Creating a Runnable Interface
A
Runnable is a Java Interface that only has the public void run() method which we need to override.
It acts like a Decorator for the run code which will be executed by a new Thread(Runnable someRunnableCode).
- it is better than extending
Threadbecause we can extend another Java Class or implement multiple interfaces.
public class Loop implements Runnable {
public final String label;
public Loop(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; true; i++) {
System.out.println("Thread " + label + ": " + i);
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread loop = new Thread(new Loop("1"));
loop.start();
}
}