Created: 2023-09-29 19:44
Status: #concept
Subject: Programming
Tags: Hashing bcrypt
Hash Function
A hash function acts like a black box that Hashes an arbitrarily-sized value into a deterministic fixed-size value.
- the resulting value can act like an Array index for java.util.HashMap implementations, see
.hashCode()method in Java.
It is usually mathematically denoted as
Hashing for Data Structures
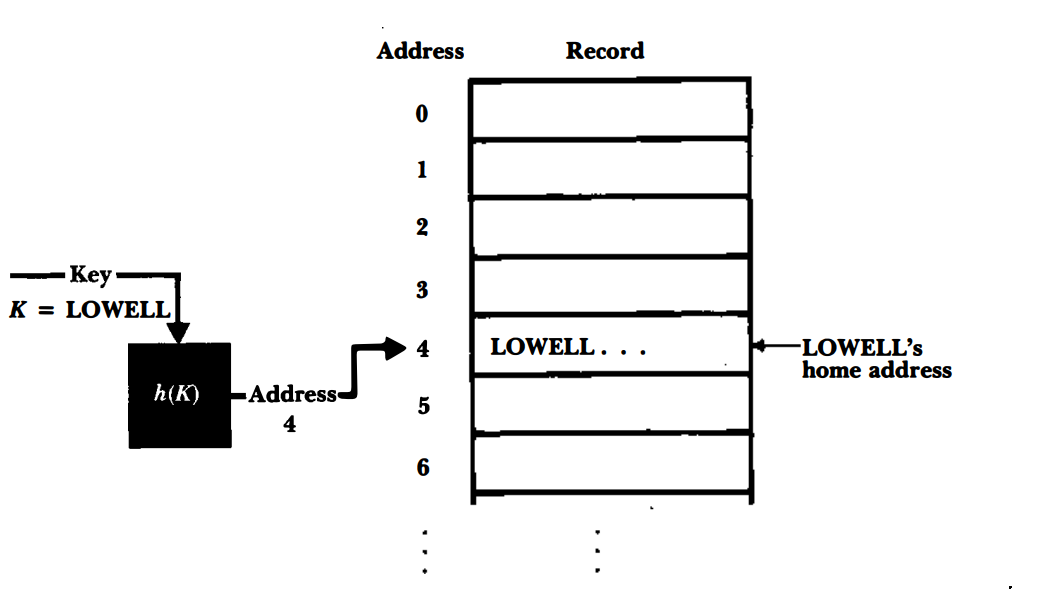
We can use hash functions to return the Memory Address or index of an element (or bucket of elements) in an array.
- this allows us to create
O(1)search, insert, and delete functions by sacrificing memory due to a specified Load Factor.
The hash function or Instance.hashCode() in java.util.HashMap should therefore return the beginning address or index to search for an element in a bucket.
- the hashing function then randomizes parameters from the input into a random value within some range like
0-9withh(x) % 10.
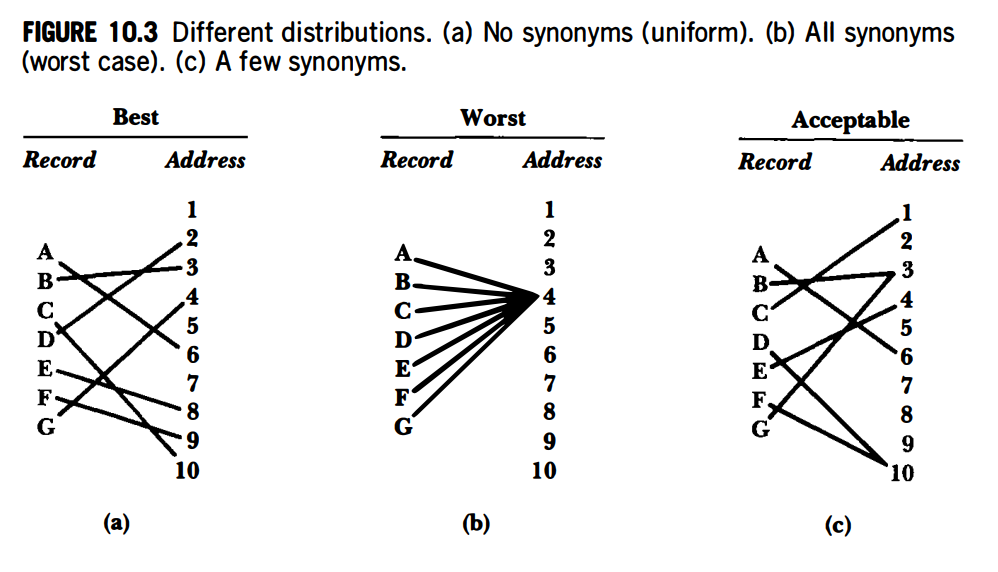
Collisions
Collisions occur when the hash function
- When this happens
and are called synonyms as they belong in the same bucket.
We have to create a holy grail hash function for our data set that produces as few collisions as possible. This holy grail should:
- Spread out records to different uniform addresses evenly.
- We want the buckets to be as small as possible for shorter access time.
- Use extra memory for storing multiple buckets.
- To reduce chances of buckets filling up, we can add more buckets by using more memory, by adding more indices.
Ideal Hash Function
A hash function that can always evenly divide data into their own indices is called a holy grail hash function.
- we use Odd Prime Numbers to create less collisions.
public int hashCode() {
int salt = 7;
int hashNumber = this.valueToHash * 31 + salt;
return hashNumber;
}
The value 31 was chosen because it is an odd prime. If it were even and the multiplication overflowed, information would be lost, as multiplication by 2 is equivalent to shifting. The advantage of using a prime is less clear, but it is traditional. A nice property of 31 is that the multiplication can be replaced by a shift and a subtraction for better performance:
31 * i == (i << 5) - i. Modern VMs do this sort of optimization automatically.From Effective Java, 2nd Edition.
Resolving Collisions
It is inevitable that collisions may occur, especially if the hash function is not ideal.
Programmers must take these into account and still add the data anyway.
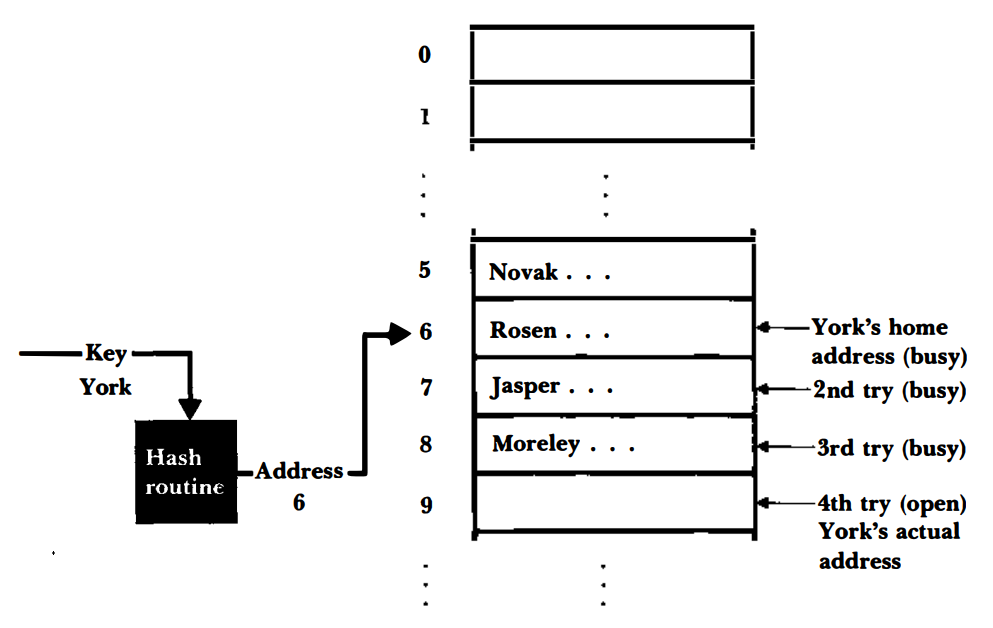
Progressive Overflow
We search for an
EMPTY bucket to insert into right after the original occupied target index.
- also known as Linear Probing.
References
- File Structures by Michael J. Folk, Chapter 10.1.1
- StackOverflow: Best Implementation for hashCode