Created: 2023-01-10 15:58
Status: #concept
Subject: Programming
Tags: Linux Memory Address Pointer Operating System
C
A low-level Programming Language created by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix.
- It is notoriously used in Embedded Systems, Compilers, and Operating Systems like Linux.
Basic Anatomy of a C Program
We declare a
main Function which is automatically invoked when we run a compiled C program like ./program.exe.
./means we check the.current Path's/directory for a file namedprogram.exe.
int main(void)
{
statements;
}
Directives
They are program editing commands (Preprocessor commands) that modify the program contents prior to compilation into an executable.
#include <stdio.h>
/* This directive states that all the code in <stdio.h> is to be "included" or concatenated into the program before it is compiled */
Statements
They are commands that are performed when the program is run and are parsed by the compiler via the program's tokens.
- this excludes Comments.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("To C, or not to C: that is the question.\n");
return 0;
}
\nis a special Escape Sequence that is common to many programming langauges to denote a new line white-space character (pressing Enter).
The main() Entry Point Function
- see IBM's main() Documentation for more info like how to accept CLI arguments to your program.
Standard Libraries
Standard libraries extend the capabilities of programming languages by including Macro Definition or Function declarations.
- they are grouped into functional domains.
- stdio.h - "standard input/ouput" for reading & printing file data and streams.
- stdin, stdout, stderr are the most common File Handle streams.
- string.h - contains utility functions for manipulating or handling strings.
- ctype.h - contains utility functions for reading, manipulating, and handling individual Characters.
- stdlib.h - contains Dynamic Memory Allocation functions like
malloc(size_t bytes). stdbool.h- contains theboolInteger data type and the Macro Definitions fortrue(1) orfalse(0) values.
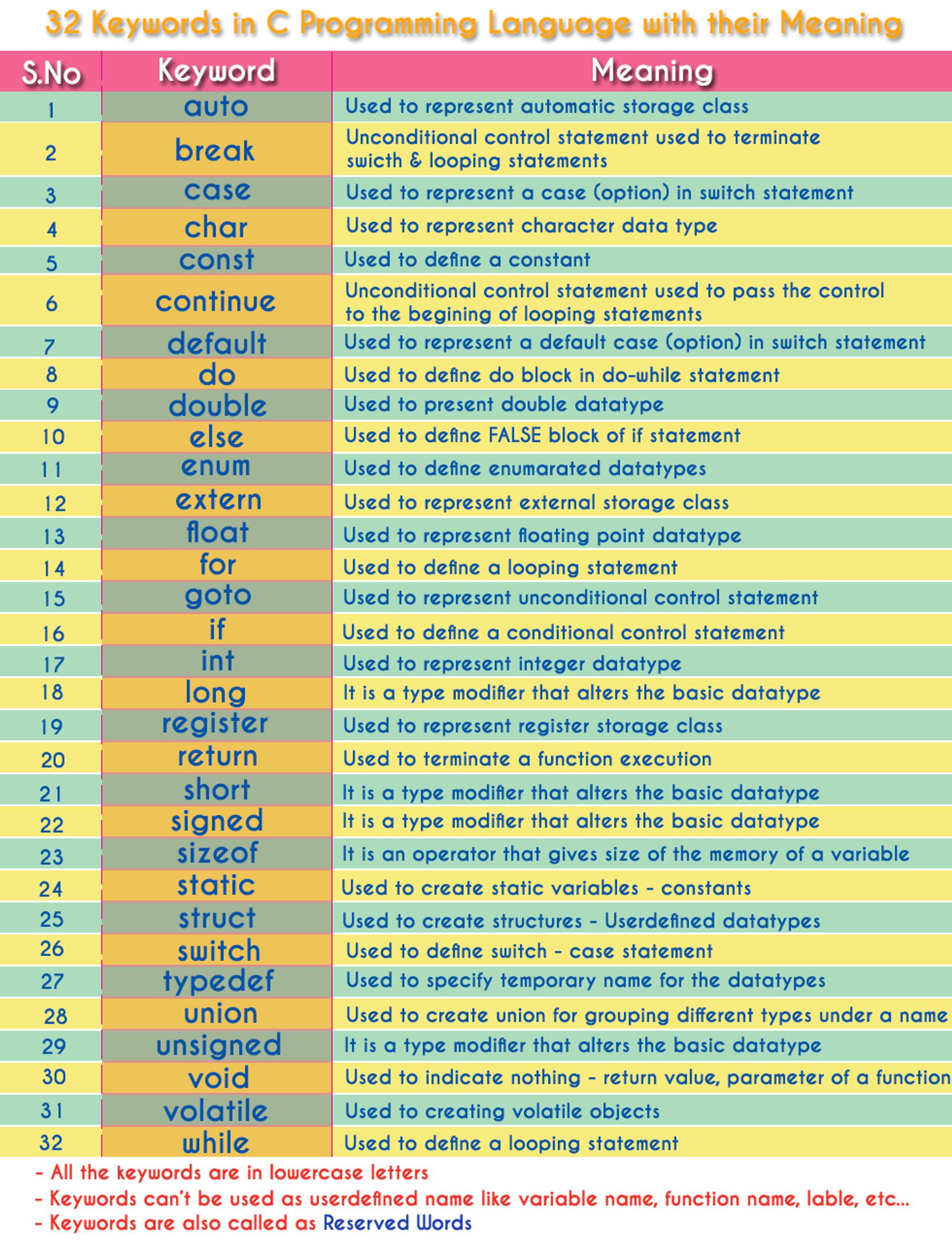
Reserved Words
We cannot use these Identifiers in C because they mean something else to the compiler.
Type Conversion System
See C Type Conversion.
Splitting Programs into Modules
We typically write our source code into
.c files while data structure declarations and Function Prototypes go into .h files.
- we compile our code with
gcc [...FILES] -o [OUTPUT_NAME]. - if we have more source code dependencies, we use Makefiles and the
makecommand.
#include <filename> // searches /lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/11/include
#include "filename" // searches the current working directory
Example
/* extern.h */
void printFoo(void);
extern int i; // used to type check or allow the source code to access 'i'
/* extern.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include "extern.h"
int i = 3; // original variable declaration
void printFoo(void)
{
printf("Foo!");
}
/* main.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include "extern.h"
int main(void)
{
printf("%d\n", i); // using 'i' without any declaration through 'extern int i'
printFoo();
}
gcc main.c extern.c -o main
./main # runs the compiled program
Using Header Guards in C
When we include the same file twice, a compilation error will occur.
- we can use Macro Definitions and compilation directives to conditionally compile code.

Reading Complex Declarations in C
There are 2 rules which comprise the Spiral Method for reading C declarations.
- First, identify the Identifier of the thing being declared and parse it going outwards.
- When there's a choice between
*or[]/(), prefer the latter first.
int *ap[10]; // an array containing 10 elements, whose types are int pointers
void (*pf)(int); // pf is a pointer to a function, with an int parameter, returning void
File Handling
See File Pointers.